LAB DIAMOND JOURNEY
Explore the two methods, namely CVD and HPHT, that can assist you in comprehending the production of lab-grown diamonds. Grasp the scientific technique that mimics the natural diamond growth process and how these processes lead to the formation of genuine lab-grown diamonds that are indistinguishable from naturally occurring ones.
The classification of Lab diamonds formation process
There are two classifications of diamonds based on their formation process. Diamonds that are formed beneath the earth's surface over billions of years through intense heat and pressure are referred to as natural mined diamonds. In contrast, man-made diamonds are produced on the earth's surface, as the name suggests, artificially. One example of man-made or lab-grown diamonds is CVD diamonds, which are created in laboratories using a specialised technique known as chemical vapor deposition.
This practical guide has been curated to provide you with an in-depth comprehension of the production method, characteristics, pricing, and other relevant aspects of lab-grown diamonds. If you're considering purchasing a CVD diamond or an engagement ring, it's worthwhile to peruse this guide.
CVD, short for chemical vapor deposition, is a process in which specific substances are deposited onto a substrate when exposed to a gas. The process involves various chemical reactions that culminate in the deposition of the material.
What is the process of creating diamonds in a laboratory?
Lab-grown diamonds are produced in a synthetic environment that replicates the natural diamond formation process beneath the Earth's mantle. Two methods are utilised for producing lab-grown diamonds, namely CVD (chemical vapor deposition) and HPHT (high pressure high temperature). Both methods are efficient in generating high-quality, genuine diamonds that are indistinguishable from naturally occurring ones.
The process of creating CVD diamonds involves using atomic hydrogen to transform graphite into diamonds. In nature, hydrogen is commonly found in the form of hydrogen molecules, which consist of two hydrogen atoms bonded together.
To produce CVD diamonds, the first step is to dissociate molecular hydrogen into atomic hydrogen. This can be achieved by utilising a gas activation agent such as an intense plasma or a hot filament.
Once the hydrogen gas is dissociated into its atoms, it is carefully applied to the substrate, which is typically graphite. The hydrogen selectively erodes the graphite surface and breaks its double bonds, causing the graphite bonds to be converted into diamond bonds.
The process begins by placing a thin seed diamond in a sealed chamber and heating it to high temperatures, generally around 800 degrees Celsius. Subsequently, hydrogen or a mixture of carbon-rich gases that includes hydrogen and methane is introduced into the chamber. By applying the methods mentioned above, the gases become ionised and their molecular bonds are broken. This results in the deposition of pure carbon onto the diamond seed, and as additional carbon atoms are formed, they form atomic bonds that are identical to those of diamonds.

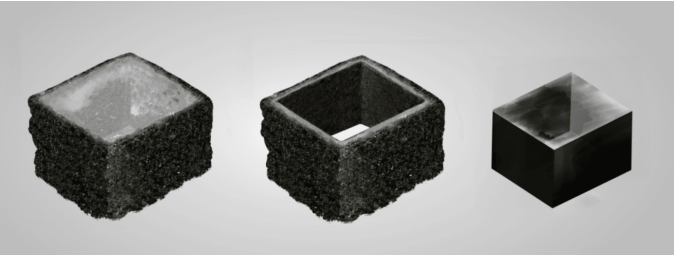
CVD DIAMOND (LEFT), HPHT DIAMOND (CENTRE), NATURAL DIAMOND (RIGHT)
Chemical Vapour Deposition (CVD) lab grown diamond
To create a lab-grown diamond using the CVD method, a thin slice of already-created lab diamond is typically chosen, measuring around 12x12mm and 300 microns thick. This slice is carefully cleaned to prevent any defects, as these can lead to inclusions in the growing diamond.
The cleaned diamond slice is then placed into a sealed chamber, where it is exposed to a carbon-rich gas at extreme temperatures. While nitrogen can be added to speed up the process, high-quality synthetic diamond producers avoid this because it can cause the diamond to develop a yellow hue.
Over a period of several weeks, the gas in the chamber breaks down and bonds with the diamond slice, gradually building up its carat weight. The resulting rough diamond has a square-cube shape.
The rough diamond is then cut with laser precision and polished using traditional techniques to achieve the desired shape. Afterward, the lab-grown diamond undergoes certification, during which graders from world famous labs organisations like GIA and IGI evaluate factors such as cut, colour, clarity, and carat weight to confirm that the diamond was created through the CVD process.
Here are 10 steps of the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process for creating lab-grown diamonds:
- 1. Diamond Seed Selection: A small diamond seed is selected as the starting point for the growth of a new diamond.
- 2. Cleaning: The diamond seed is thoroughly cleaned to ensure that it is free from any contaminants that could interfere with the growth of the new diamond.
- 3. Loading the Diamond Seed: The diamond seed is placed inside a CVD chamber.
- 4. Pumping Down: The chamber is pumped down to create a vacuum.
- 5. Introducing the Precursor Gas: A gas containing carbon (typically methane) is introduced into the chamber.
- 6. Creating Plasma: The gas is ionised to create plasma, which provides the energy necessary to break down the gas molecules.
- 7. Deposition: The carbon atoms in the plasma are deposited onto the diamond seed, gradually building up a new diamond layer by layer.
- 8. Growth Monitoring: The growth of the diamond is carefully monitored to ensure that it is proceeding correctly.
- 9. Cutting and Polishing: Once the diamond has reached the desired size, it is cut and polished into the desired shape.
- 10. Quality Control: The lab-grown diamond undergoes various quality control measures, including grading for colour, clarity, cut, and carat weight.
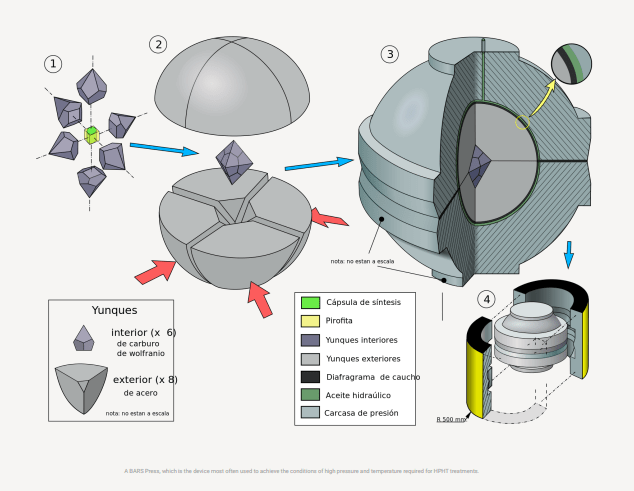
High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT) process
Creating an HPHT lab diamond involves a series of steps that require expertise, precision, and specialised equipment. HPHT is a process in which pure carbon is subjected to intense heat and pressure within a metal cube by using electric pulses. The carbon eventually breaks down and crystallises into a diamond. Any metal residues within an HPHT diamond are usually microscopic and not easily visible.
According to most experts, HPHT diamonds are of higher quality than CVD diamonds. CVD diamonds are produced quickly, which can result in internal marks and graining. Additionally, CVD diamonds often have a brownish hue, necessitating post-growth treatment to enhance their appearance. HPHT diamonds are generally produced to a higher standard and do not require post-growth treatment.
Similar to natural diamonds, lab diamonds undergo rigorous grading evaluations during certification by grading organisations such as GIA and IGI. Therefore, you can filter your diamond search based on the usual cut, colour, and clarity standards to find a lab diamond that is equally beautiful as a top-quality natural diamond.

Here are the ten steps involved in creating an HPHT lab diamond:
- 1. Selection of Raw Materials: Choose high-quality graphite as the source material, which has a purity of 99.9% or higher
- 2. Loading the Material: Load the graphite material into a metal capsule and add a small diamond seed.
- 3. Sealing the Capsule: The capsule is sealed and placed into a press.
- 4. Applying Pressure: Apply pressure up to 1.5 million pounds per square inch (psi) to the capsule with a hydraulic press to create the desired conditions.
- 5. Heating: Heat the capsule up to 1,500 degrees Celsius or higher, with the help of electric pulses.
- 6. Graphitisation: Graphitisation occurs at this stage as the graphite material transforms into diamond form under high pressure and high temperature.
- 7. Growing the Diamond: Growing the diamond continues until it reaches the required size.
- 8. Cooling the Capsule: Allow the capsule to cool down slowly.
- 9. Removing the Diamond: Remove the diamond from the capsule.
- 10. Polishing the Diamond: Polish the rough diamond to achieve the desired shape and clarity.
These ten steps are the primary steps in creating an HPHT lab diamond, although there may be variations depending on the specific process used.
CVD VS HPHT DIAMONDS
In general, HPHT diamonds are considered to have superior aesthetics and are often regarded as higher quality compared to diamonds produced through other methods. On the other hand, the CVD process is often promoted as the superior method due to its speed, cost-effectiveness, and lower energy usage. However, the truth is that this rapid process tends to result in diamonds of lower quality, which may exhibit undesirable features such as brownish hues, irregular inclusions, and internal graining. To address these flaws, CVD diamonds may undergo post-growth HPHT treatment, but this can sometimes result in a milky or hazy appearance.The scientific differences between CVD and HPHT lab diamonds are evident and significant.
-

- CVD
- CUBIC
- 1 GROWTH
- EVEN COLOUR
- NO
- GRAPHITE OR OTHER MINERAL
- BANDED
- UNUSUAL
- OCCASIONAL
-
APPEARANCE
- PROPERTIES
- SHAPE
- DIRECTION
- DISTRIBUTION
- GRANNING PATTERN
- INCLUSION
- STRAIN PATTERN
- FLUORESCENCE
- PHOSPHORESCENCE
-

- HPHT
- CUBOCTAHEDRON
- 14 GROWTH
- 2GEOMETRIC COLOR ZONING .EVEN
- GRANNING
- METALLIC
- NO
- UNUSUAL
- OCCASIONAL
EXPERT CONSULTATION
A complimentary, no-obligation consultation with your personal design consultant.
We have a team of diamond and design experts ready to assist you at every stage of the process. From comprehending the nuances of carat weight, colour, cut, and clarity to creating the ideal design, our experts are here to provide guidance and support.
WE ARE HERE TO HELP
Whether you prefer online or in-store consultations, our team of diamond and design experts are ready to assist you every step of the way.
One-to-one consultation is the best service to explore more.

GUIDANCE
Explore our comprehensive and informative guides covering a wide range of topics. Don't hesitate to ask questions and delve deeper into your interests. Let your curiosity guide you and discover something that truly resonates with you.
LAB DIAMONDS
Learn about lab grown diamond from pout detailed guide. Discover how lab diamond is created.
NATURAL Vs LAB DIAMONDS
Lab diamonds are 100% real diamonds, possessing optical, chemical, and physical properties identical to those of naturally mined diamonds.
LAB DIAMONDS JOURNEY
Explore the lab diamond’s price and value propositions. Discover how lab diamond is evaluated.



